While Windows Server 2012 R2 is an essential tool for virtualization solutions, its installation is complex and time-consuming. IT administrators have to be well-trained in virtualization concepts. In addition to the regular software, extra components have to be installed. For instance, the load balancer is not installed automatically and requires NLB components. As the features of Windows Server 2012 R2 cannot be used on standalone servers, an active directory domain is required.
To publish an application remotely, another tool called RemoteApp has to be installed. Moreover, a lengthy procedure must be followed to publish an application. Filtering of connections is based only on users and groups from the active directory list. There is no centralized location for backups and restores, and administrators have to perform backups individually. Windows Server 2012 R2 does not support the expansion of a server farm into various geographical locations.
Microsoft Server 2012 R2, the server version of the Windows OS, comes with several innovative features. Remote Desktop Services is a notable feature that offers businesses the ability to publish desktops and applications to remote users securely. Another important enhancement in Windows Server 2012 R2 is the improved Hyper-V performance. This feature-rich virtualization platform helps organizations optimize costs and achieve operational efficiencies. The high scalability of Hyper-V provides virtualization support for 320 logical processors, and 4 TB of physical memory with 1024 VMs per host. It also supports 64-node clusters that can host 8000 VMs per client.
Microsoft has done a lot to improve how Hyper-V works in a private cloud, with features like Shared VHDX files that make it easier to separate storage and compute, and to quickly migrate a virtual machine from one server to another. Live migration now supports migration between different base operating systems, as well as using compression to significantly speed up transfers. There's also support for deduplication in virtual disks, which in conjunction with improved caching speeds up booting virtual machines — something that's key to delivering improved VDI performance to your end users. Windows Server 2012 R2 is a proven, enterprise-class cloud and data centre platform that can scale to run your largest workloads while enabling robust recovery options to protect against service outages. It helps accelerate time to value by simplifying your underlying infrastructure and allowing you to reduce cost by taking advantage of the industry-standard hardware. Windows Server 2012 R2 helps you build, deploy and scale applications and websites quickly, and gives you the flexibility to move workloads between on-premises environments and the cloud.
It enables you to provide flexible, remote access to corporate resources while managing identities across your datacenter and federated into the cloud, and it helps you protect critical business information. You can free download the Windows server 2012 R2 ISO file from the below direct link. Windows Server 2012 R2 is configured, like Server 2012, via Server Manager. It's a modern-style desktop application that gives you an overview of running services from its dashboard, as well as launching the familiar Windows Server management tools and handling role and feature installation. It's a useful one-stop shop for managing one or many servers, although for more complex tasks you'll want to use PowerShell or System Center 2012 R2.
With DSC you can define the managed elements of a server or a service, and can ensure they always have the correct configuration. One of the most significant new features in Server 2012 R2 is Workplace Join. Best thought of as a granular version of full Active Directory membership, joining a workplace lets lightly-managed devices (like a Windows RT tablet, or a user's own PC) access files and directories. Workplace Join creates an Active Directory entry for the device, and delivers an authentication certificate that can be used to give access to files on corporate servers — without having to join a domain.
There's also an option for users to choose to add a Workplace Joined device to Windows Intune or System Center 2012 R2 Configuration manager, to provide additional management capabilities. Microsoft's 'Blue' wave of tools and technologies is more than just a user interface refresh. It's the next step on Microsoft's journey to becoming a devices and services company, and the first of what the company intends to be a regular series of updates to its core platform. Improved reliability for on-disk structuresReFS uses B+ trees for all on-disk structures including metadata and file data.
Metadata and file data are organized into tables similar to a relational database. Free space is counted by a hierarchical allocator which includes three separate tables for large, medium, and small chunks. All ReFS metadata has built-in 64-bit checksums which are stored independently. If nevertheless file data or metadata becomes corrupt, the file can be deleted without taking the whole volume offline. ReFS seamlessly integrates with Storage Spaces, a storage virtualization layer that allows data mirroring and striping, as well as sharing storage pools between machines.
Support for named streams is not implemented in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, though it was later added in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2. Dynamic disks with mirrored or striped volumes are replaced with mirrored or striped storage pools provided by Storage Spaces. In Windows Server 2012, automated error-correction with integrity streams is only supported on mirrored spaces; automatic recovery on parity spaces was added in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
In November 2013, Microsoft released the R2 version of Windows Server Essentials, along with other editions of Windows Server 2012 R2. Interestingly, in Windows Server 2012 R2, the company provides the ability to install the "Windows Server Essentials Experience" as a server role when you install the Standard or Datacenter edition. With Windows Server standard 2012 R2, you run your most important work volumes with robust recovery options. You benefit quickly from optimum value through a wide range, low cost, high performance storage options and simplified delivery of IT services for multiple tenants. You can build applications on site and in the cloud, deploy, manage and monitor.
And with a Server 2012 R2 Standard license you provide users with secure access to corporate resources from any device. With cyberattacks on the rise, running apps and data on an unsecured or unsupported version can create significant security risks. If you want to experience better performance, efficiency, and much needed security updates, then it is highly recommended to upgrade to the most current version.
You have the option of purchasing extended security updates, which will buy you a little more time on your current version. You also have the option of upgrading to the newest version of Windows Server, which is 2019. Windows Server 2012 is the sixth version of the Windows Server operating system by Microsoft, as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It is the server version of Windows based on Windows 8 and succeeds Windows Server 2008 R2, which is derived from the Windows 7 codebase, released nearly three years earlier.
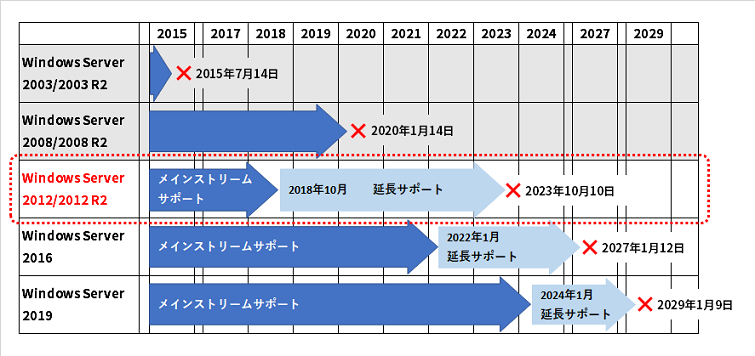
Is Windows Server 12 Free Two pre-release versions, a developer preview and a beta version, were released during development. The software was officially launched on September 4, 2012, two months before the release of Windows 8. A successor was released on October 18, 2013, entitled Windows Server 2012 R2. Microsoft ended mainstream support for Windows Server 2012 on October 9, 2018, and extended support will end on October 10, 2023.
As well as being released more often, these SAC versions don't have as many user interface features as the LTSC Windows Server editions. The SAC versions are also integrated into Microsoft subscription servers in the cloud, including Azure Marketplace, Visual Studio, and Software Assurance. Although Windows Server 2012 R2 can standalone, it's now best considered in tandem with System Center 2012 R2. The two products were developed alongside each other, and System Center now serves as a control layer for the tools and services that run on Windows Server — especially around managing networks and virtual servers and applications.
The two together are the basis of a software-defined datacentre that reaches from your server to the cloud (whether it's Azure or a hosting provider's Windows Servers). Full windows server functionality with unlimited virtual instances. Easy-to-use interface, pre-configured connectivity to cloud- based services, and no virtualization rights.
Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V, as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event. Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premises connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format). Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster.
SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role. Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 has no support for Itanium-based computers, and has four editions. Various features were added or improved over Windows Server 2008 R2 , such as an updated version of Hyper-V, an IP address management role, a new version of Windows Task Manager, and ReFS, a new file system.
Window server is actually the server which is operated, installed and managed by Window Server Family. Windows Servers are efficient in providing many services like messaging, security, hosting a website, manage resources between application and user. The idea behind SBS was to take basically the same concept used by hardware makers to create multi-function machines (printer/scanner/fax/copier) and apply it to software. SBS in its various incarnations combined the Exchange email server with the SQL Server database server, Proxy Server or its successor ISA Server, and later SharePoint services. Earlier versions also included the Outlook mail client and FrontPage HTML editor. In addition you will also learn how to configure rule enforcement, rules for multiple profiles using Group Policy, Windows Firewall to allow or deny applications, scopes, ports, users, and import and export settings.
Finally you will learn to configure connection security rules, and configure authenticated firewall exceptions. Windows NT Server had additional service packs to support increasingly complicated networks, and this led to the release of Windows NT 4.0 Enterprise Server in 1997. The Microsoft Transaction Server and Message Queue enhancements were designed to handle interactions with congested networks. The updates also added the ability to manage operating systems for server clusters and provided integration for public-key encryption services. Windows NT Server 3.51 came out in 1995 to align with the regular operating system release of Windows 95.
The server version supported computers running Windows 95 and provided some improvements to make the system more stable. The upgrade also provided the ability to manage the software licenses on client computers, including installing and updating operating system elements on client computers over the network. Obviously, Microsoft's "hidden agenda" was to motivate small businesses to move their email and other server hosting needs to Office 365. Extended support refers to the latter 5 years of product support per the LTSC system.
It's no longer the focus of the Microsoft team, and will likely have been succeeded by at least one more product in the meantime. During extended support, customers will only receive critical security updates and reliability patches. Non-security hotfixes will not be delivered unless the customer has an extended support agreement with Microsoft – and that comes at a cost.
Microsoft knows not everyone has the same needs for their operating systems, which is why they have different options for Windows server versions. Some businesses don't have the capacity to upgrade to every new version, and some may not want to upgrade because new releases aren't always stable. Other companies may need more frequent updates and the latest enhancements.
Microsoft took another three years to develop significant updates to Windows Server, which were released as Windows Server 2008. This release saw more improvements to Active Directory and changes in the interaction between the operating system's software support features and network services. There's also improved support for virtual networking, with the Hyper-V Extensible Switch providing a framework for software-defined networking. If you're using Windows Server 2012 R2 to host multi-tenant applications, there's now also a multi-tenant VPN gateway to manage secure access to separate virtual networks in your datacentre. Managing those virtual IP addresses is also simplified with the addition of virtual address management to Windows Server's IP Address Management tooling. For high availability, additional gateways and servers can be added easily using a simple wizard.
Moreover, a load balancer is automatically configured in Parallels RAS. Using a centralized dashboard, you can back up and restore server configuration with a single click. As activities are logged in an audit log, customized reports can be generated. With Parallels RAS, remote users can access corporate resources from an HTML5 browser.
With just one tool, you can monitor and manage the entire virtualization infrastructure from a single dashboard. Unlike Windows Server 2012, the installation of Parallels® Remote Application Server is simple and easy. You only have to install one single msi file and virtualization knowledge is not required.
Using simple wizards, you can easily add servers and other components. To publish an application remotely, you can use a simple wizard. You can specify from which server farm the application is to be published. In addition to users and groups, connections can be filtered by MAC address, IP address, Gateway, and client address.
Parallels RAS supports one-time code authentication mechanisms such as SafeNet and DeepNet. This can improve startup times on machines that are disconnected from the company network. New Group Policy settings have been added to cover new features in Windows 8.1 and Internet Explorer 11, such as enabling/disabling SPDY/3 support, configuring start screen layouts, and detecting phone numbers in web pages. Many new features are added like network virtualization, multitenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premises connectivity, and cloud backup.
It can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory. We can active up to 1024 virtual machine per host and also we can act up to 8000 failover cluster. This version enhanced the server functionality to support interconnectivity with both Unix systems and Novell NetWare. Because Unix and Novell servers were the standards at the time, this approach was essential for Windows NT Server to be competitive in the market.
The interconnectivity meant servers with the Windows operating system could be incorporated in an existing network running on Unix or Novell. It's a modern-style desktop application that gives you an overview of running services from its dashboard, as well as launching the familiar Windows Server management tools and handling role and feature installation. This is not a major issue it now seems 16 bit support is a "Windows Feature" and requires elevation to install. Most users will be standard users, so unless this is enabled on the build, they will not be able to run the application. This is really important in a well-managed secure desktop environment, and this is one type of issues AppDNA will highlight in the Citrix AppDNA product update for Windows 8.1 support.
Microsoft has released the minimum requirements for the new operating system. If the used hardware does not meet these requirements, the installation will terminate. If you want to use Windows Server 2012 with more than the basic features and additional features and server roles, the hardware requirements will increase accordingly. Indeed, if you're familiar with the mainstream Windows Server 2012 versions -- Standard and Datacenter -- you might know that the management interface for Storage Spaces in those products is decidedly complex.



















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.